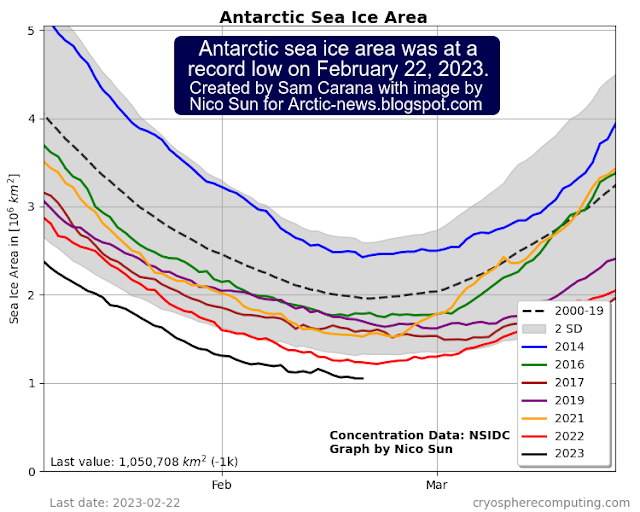
Antarctic sea ice area was 1,050,708 km² on February 22, 2023, as illustrated by the Nico Sun image below.
This means that a huge amount of heat that was previously reflected back into space by the sea ice is now instead absorbed by the Southern Ocean, in a self-reinforcing feedback loop that results in further sea ice loss, in turn further speeding up the temperature rise and making the weather ever more extreme.
Arctic sea ice extent was 14,271,000 km² on February 19, 2023, the third-lowest extent in the NSIDC record for the time of year, as illustrated by the above image.
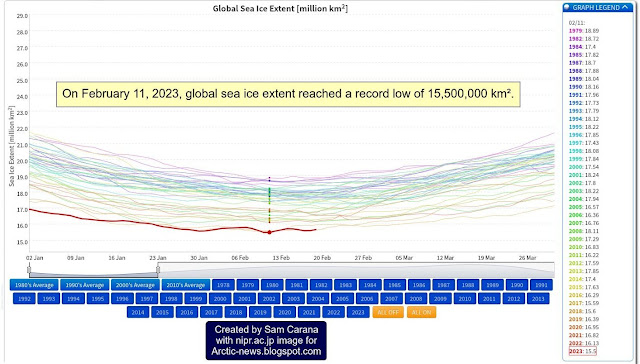
Global sea ice extent reached a record low of 15,500,000 km² on February 11, 2023, as illustrated by the above image.
The situation is dire
The dire situation is further illustrated by the image below, showing high sea surface temperature anomalies (from 1981-2011) over the Southern Ocean, the Atlantic ocean and the Arctic Ocean on February 19, 2023.
Given the dire situation regarding sea ice and sea surface temperatures, Arctic sea ice may fall dramatically later in the year.
It is remarkable for CO₂ levels to already reach record high levels this early in the year, given that CO₂ levels typically reach their annual maximum in May. This spells bad news for developments over the next few months. Keep in mind that carbon dioxide reaches its maximum warming some 10 years after emission, so we haven't been hit by the full wrath of carbon dioxide pollution yet.
The Clouds Tipping Point, at 1200 ppm CO₂e, could be crossed and this on its own could result in a further rise of 8°C. As illustrated by the above image, this tipping point could be crossed as early as in 2027 due to forcing caused by the rise in methane alone. When further forcing is taken into account, this could happen even earlier than in 2027.
This earlier post also discusses how CO₂ and heat taken up by oceans can be reduced. A 2021 study on oceans finds that, with increased stratification, heat from climate warming less effectively penetrates into the deep ocean, which contributes to further surface warming, while it also reduces the capability of the ocean to store carbon, exacerbating global surface warming. A 2022 study finds that ocean uptake of CO₂ from the atmosphere decreases as the Meridional Overturning Circulation slows down. An earlier analysis warns about growth of a layer of fresh water at the surface of the North Atlantic resulting in more ocean heat reaching the Arctic Ocean and the atmosphere over the Arctic, while a 2023 study finds that growth of a layer of fresh water decreases its alkalinity and thus its ability to take up CO₂, a feedback referred to as the Ocean Surface Tipping Point.
The above image depicts only one sequence of events, or one scenario out of many. Things may eventuate in different orders and occur simultaneously, i.e. instead of one domino tipping over the next one sequentially, many events may occur simultaneously and reinforce each other. Further events and developments could be added to the list, such as ocean stratification and stronger storms that can push large amounts of warm salty water into the Arctic Ocean.
Altogether, the rise from pre-industrial to 2026 could be more than 18.44°C, while humans are likely to go extinct with a rise of 3°C, as illustrated by the image below, from an analysis discussed in an earlier post.
Links
• NSIDC - National Snow and Ice Data Center
https://www.nsidc.org
• NSIDC - Chartic interactive sea ice graph
https://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/charctic-interactive-sea-ice-graph
• Cryosphere Computing - by Nico Sun
https://cryospherecomputing.com
• Nullschool
https://earth.nullschool.net
• Climate Reanalyzer - sea ice based on NSIDC index V3
https://climatereanalyzer.org/clim/seaice
• NOAA - Climate Prediction Center - ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions
https://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/lanina/enso_evolution-status-fcsts-web.pdf
• NOAA - Monthly temperature anomalies versus El Niño
https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/monitoring/monthly-report/global/202301/supplemental/page-4
• Blue Ocean Event
• Tropicaltidbits.com
• The Clouds Feedback and the Clouds Tipping Point
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/clouds-feedback.html
• The Importance of Methane in Climate Change
• The underappreciated role of anthropogenic sources in atmospheric soluble iron flux to the Southern Ocean - by Mingxu Liu et al. (2022)
Furthermore, emissions, ocean heat and greenhouse gas levels all keep rising.
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) at Mauna Loa, Hawaii, reached a record average daily high of 422.88 parts per million (ppm) on February 28, 2023, as illustrated by the above image and the image below.
It is remarkable for CO₂ levels to already reach record high levels this early in the year, given that CO₂ levels typically reach their annual maximum in May. This spells bad news for developments over the next few months. Keep in mind that carbon dioxide reaches its maximum warming some 10 years after emission, so we haven't been hit by the full wrath of carbon dioxide pollution yet.
Possibly even worse is the rise in methane. The image below shows NOAA globally averaged marine surface monthly mean methane data from 2016, with methane reaching 1923.57 parts per billion (ppb) in November 2022. A moving average centered over 12 months is added to highlight the acceleration in the rise in methane.
Accordingly, temperatures keep rising. An earlier analysis concludes that we have already exceeded the 2°C threshold set at the Paris Agreement in 2015.
These dire conditions spell bad news regarding the temperature rise to come, the more so since, on top of these dire conditions, there are a number of circumstances, feedbacks and further developments that make the outlook even more dire.
Circumstances that make the situation even more dire
Firstly, as illustrated by the image on the right, adapted from NOAA, we're moving into an El Niño.
It looks like it's going to be a very strong El Niño, given that we've been in a La Niña for such a long time.
It looks like it's going to be a very strong El Niño, given that we've been in a La Niña for such a long time.
Moving from the bottom of a La Niña to the peak of a strong El Niño could make a difference of more than half a degree Celsius, as illustrated by the image below, adapted from NOAA.
 |
| [ click on images to enlarge ] |
Temperature anomalies can be very high during an El Niño. The February 2016 temperature on land-only was 2.96°C above 1880-1920, and in February 2020, it was 2.79°C higher, as illustrated by the image below, created with screenshots taken on February 15, 2023. Note that 1880-1920 isn't pre-industrial.
Secondly, sunspots look set to reach a very high maximum by July 2025, as illustrated by the next two images on the right, adapted from NOAA.
Observed values for January 2023 are already well above the maximum values that NOAA predicted to be reached in July 2025.
Observed values for January 2023 are already well above the maximum values that NOAA predicted to be reached in July 2025.
If this trend continues, the rise in sunspots forcing from May 2020 to July 2025 may well make a difference of more than 0.25°C, a recent analysis found.
Thirdly, the 2022 Tonga submarine volcano eruption did add a huge amount of water vapor to the atmosphere.
Since water vapor is a potent greenhouse gas, this is further contributing to speed up the temperature rise.
A 2023 study calculates that the submarine volcano eruption near Tonga in January 2022, as also discussed at facebook, will have a warming effect of 0.12 Watts/m² over the next few years.
The image below, created with NOAA data, shows Annual Northern Hemisphere Land Temperature Anomalies and has two trends added. The blue trend, based on 1850-2022 data, points at 3°C rise by 2032. The pink trend, based on 2012-2022 data, better reflects variables such as El Niño and sunspots, showing that this could trigger a huge rise, with 3°C crossed in 2024. Anomalies are from 1901-2000 (not from pre-industrial).
Feedbacks and developments making things worse
Indeed, a huge temperature rise could be triggered, due to a multitude of feedbacks and further developments that could strongly deteriorate the situation even further.
On top of the water vapor added by the Tonga eruption, there are several feedbacks causing more water vapor to get added to the atmosphere, as discussed at Moistening Atmosphere.
Further feedbacks include additional greenhouse gas releases such as methane from the seafloor of the Arctic Ocean and methane, carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide from rapidly thawing permafrost on land.
The image below shows the Northern Hemisphere Ocean Temperature Anomaly, compared to 1901-2000. The pink trend, based on 1850-2022 data, shows that the Latent Heat Tipping Point (at 1°C) was crossed in 2022, but the red trend, based on 2007-2022 data, better reflects variables such as El Niño and shows both the Latent Heat Tipping Point and the Seafloor Methane Tipping Point (at 1.35°C) getting crossed in 2024.
Ominously, November 2023 temperature anomalies are forecast to be at the top end of the scale for a large part of the Arctic Ocean, as illustrated by the tropicaltidbits.com image below.
Some developments could make things even worse and a huge temperature rise could unfold soon. The image below shows a polynomial trend added to NOAA globally averaged marine surface monthly mean methane data from April 2018 to November 2022, pointing at 1200 ppm CO₂e (carbon dioxide equivalent) getting crossed in 2027.
On top of the February 28, 2023 daily average of 422.88 ppm for CO₂, methane can add 384.71 ppm CO₂e when using a 1-year GWP of 200 for NOAA's 1923.57 ppb November 2022 methane mean.
While methane at higher altitude can reach even higher levels than NOAA's marine surface data, adding NOAA's November 2022 mean to 422.88 ppm CO₂ would leave just 392.41 ppm CO₂e for further forcing, before the Clouds Tipping Point would get crossed, as the image on the right illustrates.
While methane at higher altitude can reach even higher levels than NOAA's marine surface data, adding NOAA's November 2022 mean to 422.88 ppm CO₂ would leave just 392.41 ppm CO₂e for further forcing, before the Clouds Tipping Point would get crossed, as the image on the right illustrates.
 |
| [ see the Extinction page ] |
Further forcing comes from nitrous oxide and other greenhouse gases, while rises in other gases and further changes such as caused by sea ice loss and changes in aerosols can also speed up the temperature rise.
Changes in aerosols are discussed in earlier posts such as this post and this post. The upcoming temperature rise on land on the Northern Hemisphere could be so strong that much traffic, transport and industrial activity will grind to a halt, resulting in a reduction in cooling aerosols that are now masking the full wrath of global heating. These are mainly sulfates, but burning of fossil fuel and biomass also emits iron that helps photosynthesis of phytoplankton in oceans, as a 2022 study points out.
The image on the right, from the extinction page, includes a potential rise of 1.9°C by 2026 as the sulfate cooling effect falls away and an additional rise of 0.6°C due to an increase in warming aerosols by 2026, as discussed in this post and earlier posts.
Without these emissions, the temperature is projected to rise strongly, while there could be an additional temperature rise due to an increase in warming aerosols and gases as a result of more biomass and waste burning and forest fires.
The image on the right indicates that the rise from pre-industrial to 2020 could be as much as 2.29°C. Earth's energy imbalance has grown since 2020. Therefore, the rise up to now may be higher.
Climate Tipping Points and further Events and Developments
The temperature could also be pushed up further due to reductions in the carbon sink on land. An earlier post mentions a study that found that the Amazon rainforest is no longer a sink, but has become a source, contributing to warming the planet instead; another study found that soil bacteria release CO₂ that was previously thought to remain trapped by iron; another study found that forest soil carbon does not increase with higher CO₂ levels; another study found that forests' long-term capacity to store carbon is dropping in regions with extreme annual fires; another earlier post discussed the Terrestrial Biosphere Temperature Tipping Point, coined in a study finding that at higher temperatures, respiration rates continue to rise in contrast to sharply declining rates of photosynthesis, which under business-as-usual emissions would nearly halve the land sink strength by as early as 2040.
This earlier post also discusses how CO₂ and heat taken up by oceans can be reduced. A 2021 study on oceans finds that, with increased stratification, heat from climate warming less effectively penetrates into the deep ocean, which contributes to further surface warming, while it also reduces the capability of the ocean to store carbon, exacerbating global surface warming. A 2022 study finds that ocean uptake of CO₂ from the atmosphere decreases as the Meridional Overturning Circulation slows down. An earlier analysis warns about growth of a layer of fresh water at the surface of the North Atlantic resulting in more ocean heat reaching the Arctic Ocean and the atmosphere over the Arctic, while a 2023 study finds that growth of a layer of fresh water decreases its alkalinity and thus its ability to take up CO₂, a feedback referred to as the Ocean Surface Tipping Point.
 |
| [ from Blue Ocean Event 2022? - click on images to enlarge ] |
The above image depicts only one sequence of events, or one scenario out of many. Things may eventuate in different orders and occur simultaneously, i.e. instead of one domino tipping over the next one sequentially, many events may occur simultaneously and reinforce each other. Further events and developments could be added to the list, such as ocean stratification and stronger storms that can push large amounts of warm salty water into the Arctic Ocean.
While loss of Arctic sea ice and loss of Permafrost in Siberia and North America are often regarded as tipping points, Antarctic sea ice loss, and loss of the snow and ice cover on Greenland, on Antarctica and on mountaintops such as the Tibetan Plateau could also be seen as tipping points. Another five tipping points are:
- The Latent Heat Tipping Point
- The Seafloor Methane Tipping Point
- The Clouds Tipping Point
Extinction
Altogether, the rise from pre-industrial to 2026 could be more than 18.44°C, while humans are likely to go extinct with a rise of 3°C, as illustrated by the image below, from an analysis discussed in an earlier post.
This should act as a warning that near-term human extinction could occur sooner than most may think. Indeed, when asked what could cause humans to go extinct, many may mention:
In the video below, Edge of Extinction: Destination Destruction, Guy McPherson gives his view on our predicament.1. asteroid strikes
2. rampant pestilence, diseases, epidemics and pandemics
3. war, murder and violence
4. ecosystems and vegetation collapse, famine
5. dehydration
6. plastic pollution, spread of poisonous and toxic substances
7. nuclear accidents, nuclear war or waste leakage
8. outbreaks of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
9. emerging new or re-emerging ancient microbes
10. bio-weapons and biological experiments gone out of hand
11. infertility, genetic degeneration, loss of genetic diversity
12. madness, cults, depression and suicide
13. polar shifts, earthquakes, landslides and tsunamis
14. Artificial Intelligence gone rogue
15. hostile aliens breeding predatory animals
More recently, climate change threats are mentioned such as:
16. destructive storms, flooding, fires and more extreme weather
17. hydrogen sulfide gas released from oceans
18. depletion of the ozone layer
19. co-extinctions, i.e. extinction of species that humans depend on, resulting in our own demise.
There may be more threats, but I think the biggest threat is:
20. temperature rise
Conclusion
The dire situation we're in looks set to get even more dire, calling for comprehensive and effective action, as described in the Climate Plan and Transforming Society.
Links
• NSIDC - National Snow and Ice Data Center
https://www.nsidc.org
• NSIDC - Chartic interactive sea ice graph
https://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/charctic-interactive-sea-ice-graph
• Cryosphere Computing - by Nico Sun
https://cryospherecomputing.com
• Nullschool
https://earth.nullschool.net
• Climate Reanalyzer - sea ice based on NSIDC index V3
https://climatereanalyzer.org/clim/seaice
• NOAA - greenhouse gases - trends
• NOAA - Climate Prediction Center - ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions
https://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/lanina/enso_evolution-status-fcsts-web.pdf
• NOAA - Monthly temperature anomalies versus El Niño
https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/monitoring/monthly-report/global/202301/supplemental/page-4
• NOAA - Solar cycle progression
• NASA gistemp Monthly Mean Global Surface Temperature - Land Only
• NOAA - Annual Northern Hemisphere Land Temperature Anomalies
• Tonga eruption increases chance of temporary surface temperature anomaly above 1.5 °C - by Stuart Jenkins et al. (2023)
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41558-022-01568-2
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41558-022-01568-2
• Moistening Atmosphere
• Albedo, latent heat, insolation and more• Latent Heat
• Methane keeps rising
• A huge temperature rise threatens to unfold soon
• The Clouds Feedback and the Clouds Tipping Point
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/clouds-feedback.html
• Human Extinction by 2025?
• 2020: Hottest Year On Record
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41612-022-00250-w
• How close are we to the temperature tipping point of the terrestrial biosphere? - by Katharyn Duffy et al. (2021)
• Upper Ocean Temperatures Hit Record High in 2020 - by Lijing Cheng et al. (2021)
• Reduced CO₂ uptake and growing nutrient sequestration from slowing overturning circulation - by Yi Liu et al. (2022)
• Overshoot or Omnicide?
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41558-022-01555-7
• Cold freshwater lid on North Atlantic
• Long-Term Slowdown of Ocean Carbon Uptake by Alkalinity Dynamics - by Megumi Chikamoto et al. (2023)
• Ocean Surface Tipping Point Could Accelerate Climate Change
• When Will We Die?
• Edge of Extinction: Destination Destruction - video by Guy McPherson
• Long-Term Slowdown of Ocean Carbon Uptake by Alkalinity Dynamics - by Megumi Chikamoto et al. (2023)
• Ocean Surface Tipping Point Could Accelerate Climate Change